Understanding Personality Disorder in India: Awareness, Challenges, and Treatment

Overview
A complicated and sometimes misdiagnosed category of mental health issues affecting a person’s ideas, feelings, and behaviours are known as personality disorders.
The understanding and perception of these disorders are still developing in India due to a number of important cultural, societal, and economic aspects that affect how they are perceived and handled.
This article examines the many personality disorders that are common in India, the stigma associated with them, the types of treatments that are accessible, and the need for increased knowledge and instruction.
Personality Disorders: What Are They?
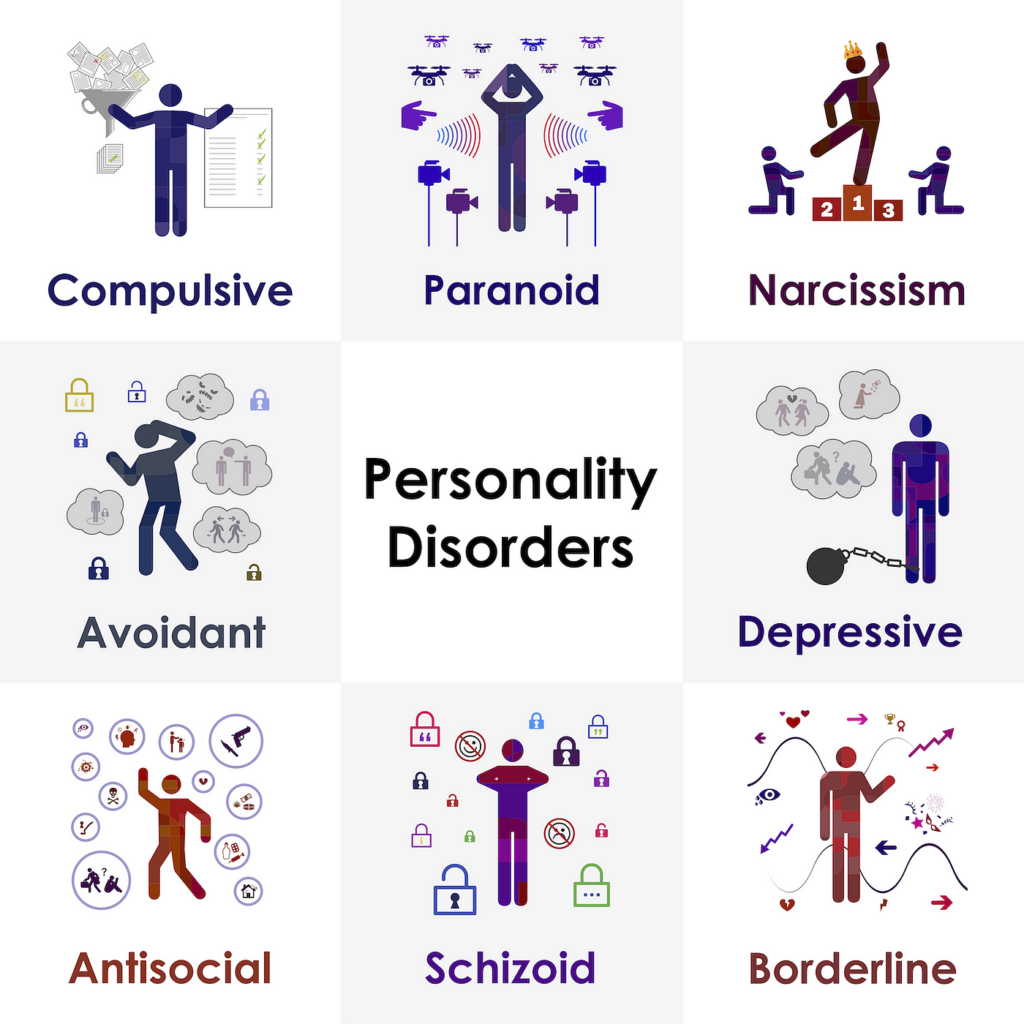
Persistent behavioural, cognitive, and interior experience patterns that substantially diverge from social norms are the hallmarks of personality disorders.
These behaviours are ubiquitous and rigid, causing anxiety or impeding social, professional, or other critical domains of functioning.
Three clusters comprise the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) classification system for personality disorders:
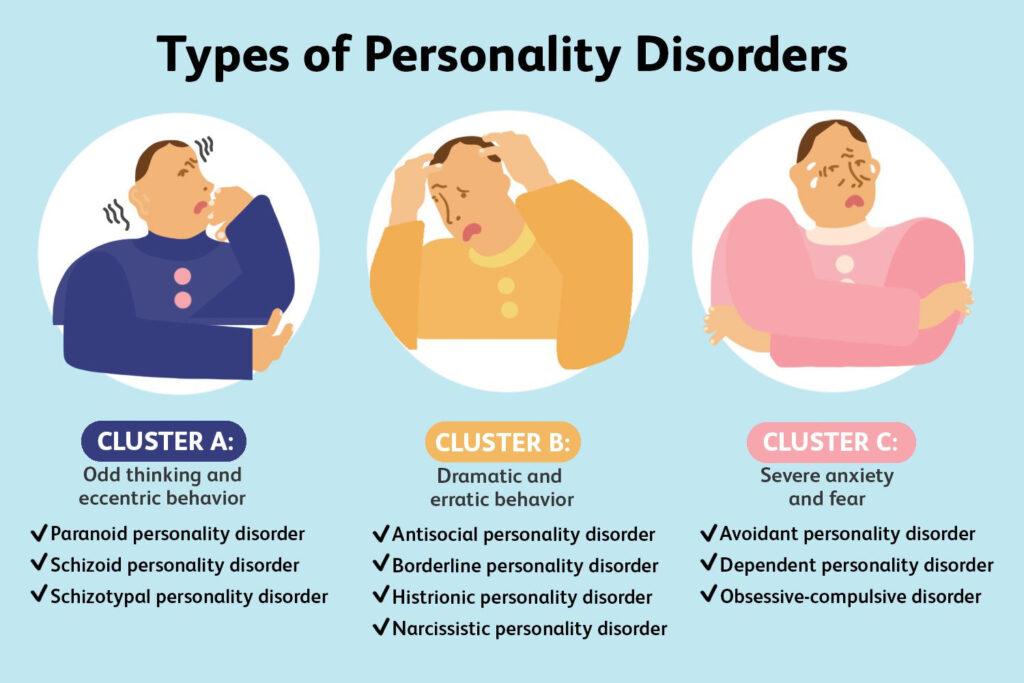
Cluster A (Strange or Eccentric): Consists of Schizoid, Schizotypal, and Paranoid Personality Disorders.
Antisocial, borderline, histrionic, and narcissistic personality disorders are included in Cluster B (dramatic, emotional, or erratic) personality disorders.
The disorders of the avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive personality types are included in Cluster C (Anxious or Fearful).
Character Disorder Prevalence in India
Although there is little data on the incidence of personality disorders in India, research does indicate that a sizable portion of the population may be affected. A demographic research carried out in urban areas revealed that 10–15% of people may have a personality disorder. These figures might be higher, though, as a lot of people might go untreated because of stigma and a lack of knowledge.
Cultural Affects : In India, cultural perspectives greatly influence the understanding of personality disorders. Due to traditional beliefs, many people seek assistance from religious leaders or healers rather than mental health experts because they believe that strange behaviours have spiritual or supernatural origins. This societal stigma may keep people from getting the necessary assistance, which can exacerbate their symptoms and set off a vicious cycle of suffering.
Typical Indian Personality Disorders
1. Personality Disorder with Borderlines (BPD)
Emotional instability, intensive interpersonal ties, and a skewed self-image are characteristics of borderline personality disorder.
The overlapping symptoms of BPD might lead to misdiagnosis of sadness or anxiety in many Indians. The identification of BPD can be made more difficult by cultural norms surrounding emotional expressiveness, which may lead people to repress their feelings, leading to heightened distress.
2. APD, or antisocial personality disorder
Antisocial Personality Disorder is characterized by a disrespect for the rights of others, deceitfulness, impulsivity, and impatience. Particularly in young people, actions linked to ASPD may be seen as delinquent or rebellious in the Indian culture.
Early intervention is essential since social and economic variables, like poverty and illiteracy, can worsen these behaviours.

3. The disorder of avoidant personality
Feelings of inadequacy, a widespread pattern of social restraint, and hypersensitivity to negative assessment are all associated with avoidant personality disorder.
In India, where social and familial bonds are strong, avoidant personalities can cause serious pain. Misconceptions regarding their challenges may arise from the perception that they are shy or introverted.
4. Personality Disorder with Narcissism
The symptoms of narcissistic personality disorder include an exaggerated feeling of one’s own significance, a craving for approval, and a lack of empathy.
In a culture that frequently places a high value on accomplishment and status, some people may display narcissistic features without fully satisfying the diagnostic criteria for the illness. This may make it more difficult to comprehend and treat these people.
The Function of Shame

In India, stigma related to mental health issues, particularly personality disorders, poses a serious obstacle to receiving treatment. Misconceptions regarding mental illness can result in social isolation and discrimination.
Many people are afraid of being called “weak” or “crazy,” which makes them reluctant to ask for assistance. Families may be impacted by this stigma, which can cause humiliation and alienation.
Expectations in Culture and Gender
The conversation of personality disorders is further complicated by gender norms in India. Women may experience additional stigma if they display emotional anguish because of societal standards that generally require them to be selfless and loving.
On the other hand, cultural expectations of masculinity may deter males from getting treatment, which could result in untreated mental health problems.
Care and Assistance

Availability of Mental Health Services
There is still little access to high-quality mental health care in India, despite the country’s growing awareness of mental health issues.
A lack of mental health providers, particularly in remote places, results in many people not getting the care they require. There are still a lot of gaps in the primary health care system despite continued efforts to integrate mental health treatments.
Medicinal Strategies
The usual course of treatment for personality disorders is either medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of the two.
Commonly employed therapeutic modalities include dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), psychodynamic therapy, and cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT). However, depending on the patient’s unique circumstances and cultural background, these treatments may or may not be beneficial.
Community Resources and Support Groups
For those with personality disorders, support groups are essential to their healing process. These groups offer a secure environment where people may talk about their experiences and gain knowledge from one another.
Community resources are crucial for lowering stigma and fostering understanding. These include mental health awareness campaigns and educational initiatives.
The Significance of Knowledge and Instruction
Reducing stigma and enhancing treatment accessibility in India need raising awareness and educating people about personality disorders. In order to promote mental health literacy, businesses, schools, and community organisations may all make a significant contribution.
Plans and Projects
In India, a number of organisations are attempting to increase public awareness of mental health issues, particularly personality disorders.
Public awareness campaigns regarding the telltale signs and symptoms of these conditions can contribute to the development of empathy and understanding.
Governmental organisations, nonprofits, and mental health specialists must work together to create a more encouraging atmosphere for those who are dealing with these issues.
Conclusion
In India, personality disorders represent a serious mental health issue that needs to be better understood and treated appropriately.
Even while cultural influences are very important in determining how these disorders are perceived, reducing stigma and expanding access to mental health services can help those who are impacted by these conditions get better results.
India can make significant progress in improving the lives of people with personality disorders by advancing education and creating supportive communities.



