What is anxiety

Anxiety is a widespread and intricate disorder that impacts millions of individuals globally. It affects daily life and general well-being profoundly; it’s not merely a sensation of uneasiness or tension.
We’ll examine the nature of worry, its causes and effects, and practical methods for controlling and reducing its symptoms in this extensive book.
What is the nature of anxiety?
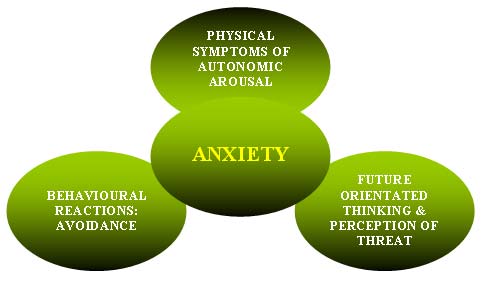
Emotional states of tension, worry, and apprehension are indicative of fear. Physical signs like sweating, shaking, and elevated heart rate are frequently present.
Although apprehension is a natural reaction to stress and can be helpful in moderation—keeping us vigilant in risky situations or inspiring us to prepare for challenges—excessive anxiety can become crippling and interfere with daily functioning.
Anxiety Disorder Types

There are many different types of tension disorders, and each has its unique set of symptoms and triggers. It can be easier to recognise and treat stress disorders if one is aware of their many forms.
The hallmark of generalised anguish disorder (GAD) is excessive and ongoing concern over a variety of life issues, including relationships with others, job, and health. Frequently, this fear is out of proportion to the chance that the dreaded events will actually occur.
Panic Disorder: Characterised by sudden and recurrent episodes of extreme terror, known as panic attacks, which can accompany physical symptoms such dizziness, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and palpitations.
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) is characterised by a severe fear of social settings and the potential for embarrassment or judgement. This may cause one to steer clear of social interactions and significant distress.
Particular phobias: Defined by a strong, illogical fear of a particular thing or circumstance, such as spiders, heights, or flying. Avoidance behaviour is often the result of the dread.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Characterised by recurring, bothersome thoughts known as obsessions and repetitive actions or thoughts known as compulsions that are carried out in an attempt to reduce the discomfort brought on by the obsessions.
A terrible event is experienced or witnessed, and then one develops post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Flashbacks, nightmares, and excruciating panic associated with the trauma are among the symptoms.
Similar to PTSD, Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) manifests symptoms three days to one month after the traumatic event.
Reasons for Uncertainty

A number of factors, including genetic, biochemical, environmental, and psychological ones, can contribute to the development of jitters disorders. Let’s examine these key elements in more detail:
Genetic Factors: stress and other mental health issues are more likely to run in families where angst is present. Research indicates that a person’s susceptibility to dread may be influenced by their genetic makeup.
Brain Chemistry: worry may be exacerbated by imbalances in neurotransmitters, which are chemicals in the brain that control mood and stress reactions. Alpha-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine, and serotonin are the main neurotransmitters linked to uneasiness.
Personality Traits: Some people are more prone to tension than others, such as those with high degrees of neuroticism or a propensity for excessive perfection.
Trauma and Stress: Panic can be brought on by or made worse by exposure to traumatic experiences, ongoing stress, or significant life changes. Adversity in childhood, abuse, or major life events like divorce or losing one’s career can all lead to the development of jitters.
Health Conditions: Fear symptoms can be brought on by or made worse by a number of illnesses, including thyroid issues, heart disease, and respiratory ailments. Substance addiction or withdrawal may also play a role.
Cognitive Factors: Worrying excessively or catastrophising are examples of negative thought processes that can exacerbate and prolong angst. Anxious people may be more sensitive to perceived threats and have a propensity to exaggerate their likelihood.
Anxiety's effects
Anxiety affects more than simply emotional pain; it can have an impact on a number of areas of life.
Physical Health: Headaches, gastrointestinal problems, tense muscles, and exhaustion are just a few of the physical symptoms that can result from long-term anxiety. Long-term stress can also impair immunity, increasing a person’s susceptibility to disease.
Mental Health: Conditions such as depression frequently coexist with anxiety. The enduring quality of worry can intensify depressive symptoms and lead to hopelessness.
Daily Functioning: Anxiety can cause problems with day-to-day functioning, making it difficult to complete duties at home, at work, or at school. People may choose to avoid particular locations or events, which can have an effect on their social and professional lives.
Relationships: Anxiety can sour ties with friends, family, and coworkers. Tension and misunderstandings might arise from avoidance behaviours, the need for reassurance, or an overwhelming concern about other people’s opinions.
Quality of Life: Anxiety’s persistent condition of fear and worry can lower one’s general quality of life. Personal fulfilment, leisure time, and enjoyment of hobbies could all be jeopardised.
Techniques for Handling Anxiety

A combination of therapy interventions, self-care techniques, and, in certain situations, medication is used to manage stress.
The following practical methods can be used to control and lessen the symptoms of anxiety:
Cognitive behavioural therapy, or CBT, is an extensively utilised, empirically supported therapeutic approach that assists people in recognising and confronting unfavourable thought patterns and behaviours linked to worry. People can create better coping strategies by altering these tendencies
.
Meditation and mindfulness: By concentrating on the present moment rather than worrying about the past or the future, mindfulness exercises and meditation can help people stay present and lower their tension levels. Relaxation can be enhanced by methods including progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and deep breathing.
Exercise: Studies have indicated that regular exercise helps elevate mood and lower anxiety. Endorphins are naturally occurring mood enhancers and stress relievers that are released during exercise. Exercises like swimming, yoga, jogging, and walking can be advantageous.
Healthy Lifestyle: Reducing symptoms of panic and promoting general well-being can be achieved by eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and abstaining from excessive caffeine and alcohol. Healthy self-care routines promote emotional and physical well-being.
Social Support: Making connections with loved ones, friends, or support groups can help to lessen feelings of loneliness and offer emotional support. It might be comforting to hear other people’s stories and get understanding from them.
Professional Assistance: Getting assistance from a psychologist, psychiatrist, or counsellor is a critical step in managing anxiety. If necessary, professionals can offer medication, therapy, and customised treatment programs.

Medication: To treat the symptoms of dread, a doctor may occasionally prescribe medication. Benzodiazepines, beta-blockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are examples of common drugs. It is important to use medication under a healthcare provider’s supervision at all times.
Avoiding Stress Triggers: One way to lessen disquiet is to recognise and deal with the sources of stress in your life. This could entail establishing limits, practicing efficient time management, or altering one’s way of life to lessen stress.
Setting Achievable Goals and Dividing Tasks Into Manageable Steps: These strategies might help lessen overload. Commemorate minor victories and advancements to sustain drive and enhance self-assurance.
In summary
Fretfulness is a prevalent and frequently difficult illness that can affect many facets of life. To properly address and alleviate symptoms, one must have a thorough understanding of the condition’s causes, effects, and accessible management strategies.
Through the integration of self-care techniques, therapeutic interventions, and expert assistance, people can cultivate efficacious coping strategies and enhance their general quality of life.
In case you or someone you know is experiencing anxiety, keep in mind that assistance is accessible. Getting help from mental health specialists, practicing self-care, and interacting with encouraging groups can all be very helpful in controlling fear and leading a healthy, happy life.



